40 draw and label a segment of dna showing its helix and complementary base pairing
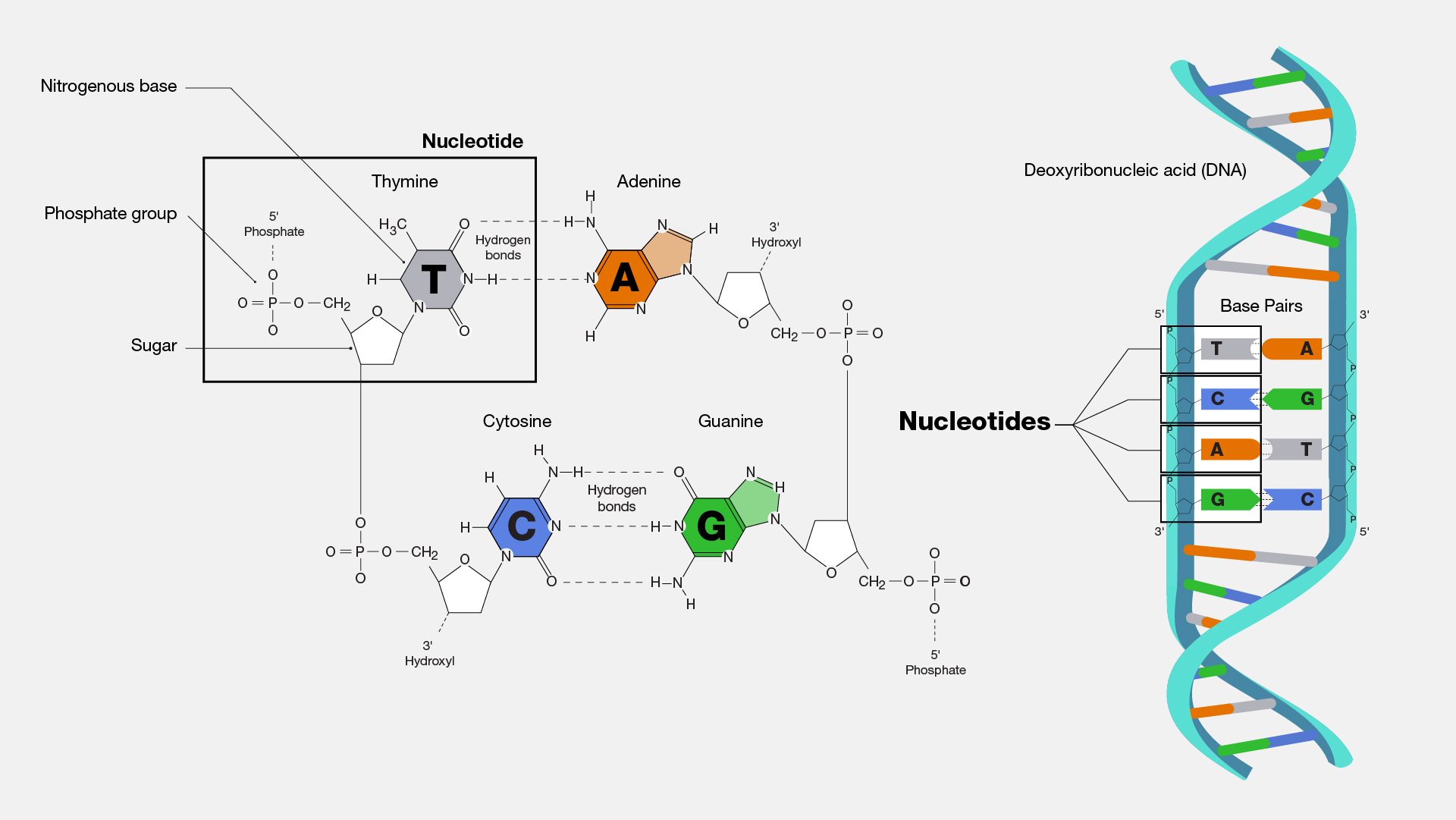
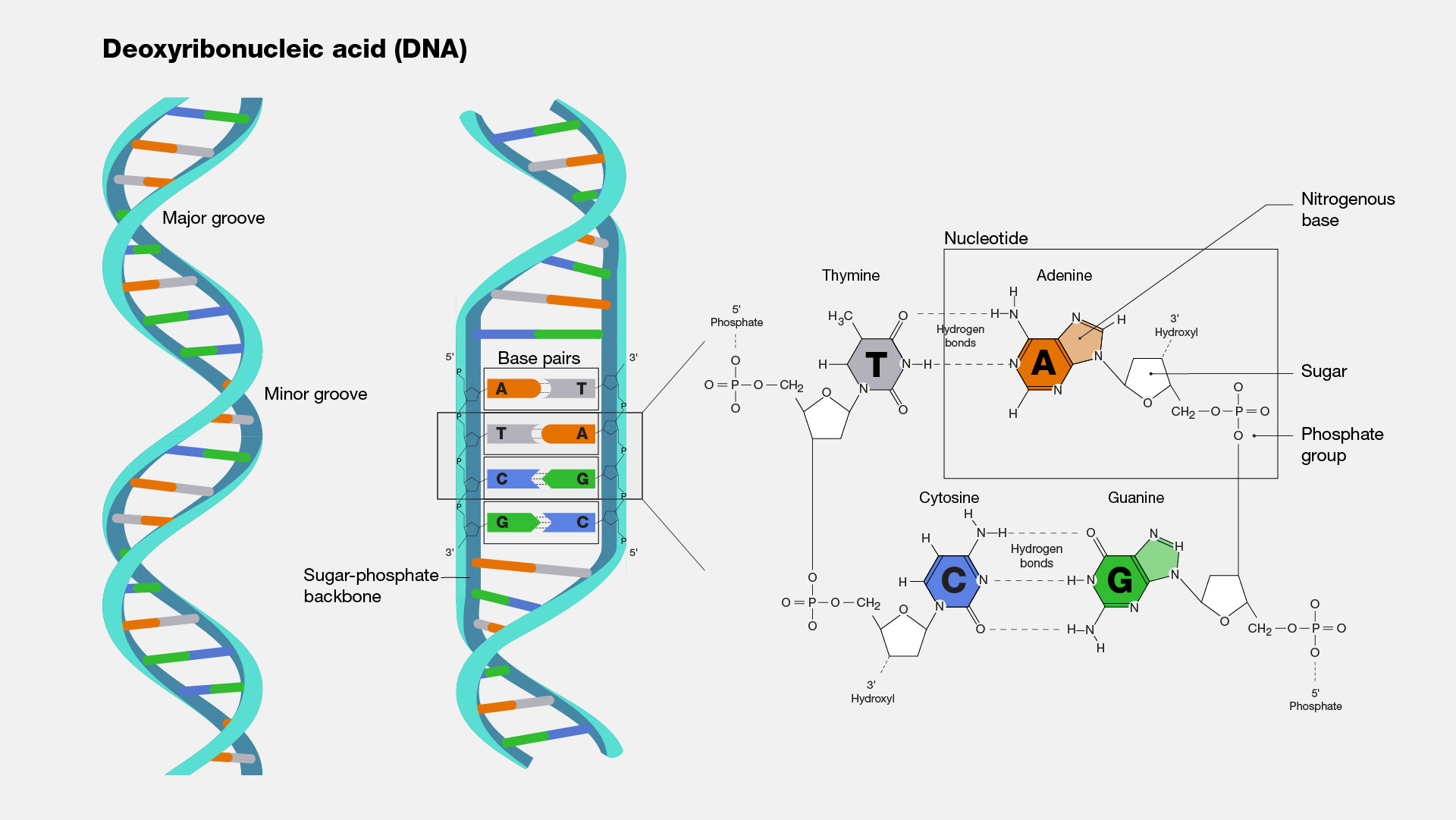
What Is the Sequence of Bases on the Complementary DNA Strand ... A nitrogenous base. DNA nucleotides can contain one of four nitrogenous bases. These bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C). These nucleotides come together to form long chains known as DNA strands. Two complementary DNA strands bond to each other in what looks like a ladder before winding into the double helix form. Draw and label a segment of DNA showing its helix and ... Image transcriptions Sugar phosphate Backbone OFF Adenine > Base Paly ,6 85 8 . M 17 18071 Thymine Nitrogenous Base evanine Cytocine Eukaryotic chromosomes consist of a DNA - protein BEAT Complex that is organized in a Compact manner which feemits the large amount of DNA to be Astored in the nucleus of the call. the Subunit designation of chromosome is Chromatin . the fundamental unit of ...
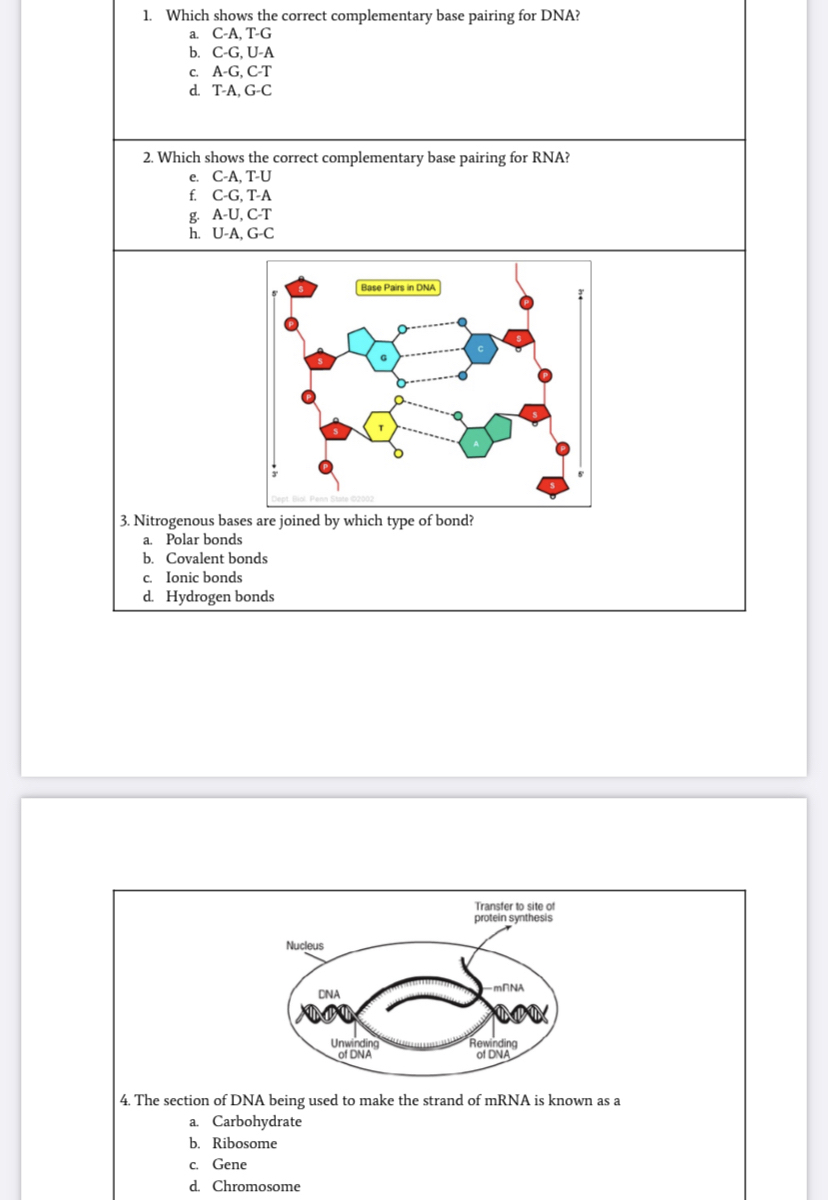
Complementary Sequences - Department of Chemistry Complementary Nucleotide Sequences. Because of the nature of complementary base pairing, if you know the sequence of one strand of DNA, you can predict the sequence of the strand that will pair with, or "complement" it. Remember, when writing complementary DNA sequences, you need to write the sequence in the 5' to 3' direction.
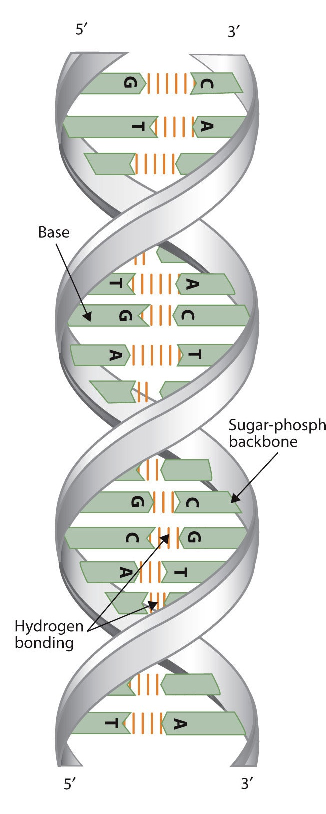
Draw and label a segment of dna showing its helix and complementary base pairing
bio pt 5 Flashcards | Quizlet radioactive labeling of bacteriophages - labeled proteins w/ radioactive phosphorus - labeled DNA w/ radioactive sulfer let the radioactive bacteriophages attack bacteria - only found traces of radioactive sulfur inside infected bacteria cells + Bacteriophage: virus that attacks bacteria RESULT: definitive evidence that DNA is genetic material Draw and label a segment of DNA showing its helix and ... Draw and label a segment of DNA showing its helix and complementary base pairing. Solution Verified Create an account to view solutions By signing up, you accept Quizlet's Terms of Service and Privacy Policy Continue with Google Continue with Facebook Sign up with email Recommended textbook solutions Biology chapter 12 section 1 - Assessment Page 332 Mylena Riera... a. It needs to replicate itself. Thus it's a double strand, and the "new" strands form on each of the old strands to form a new double helix. The base pairingsensures that the new strand will be the exact counterpart to the old strand. b. It needs to be able to store a lot of information it its molecule. It does this with only 4 bases.
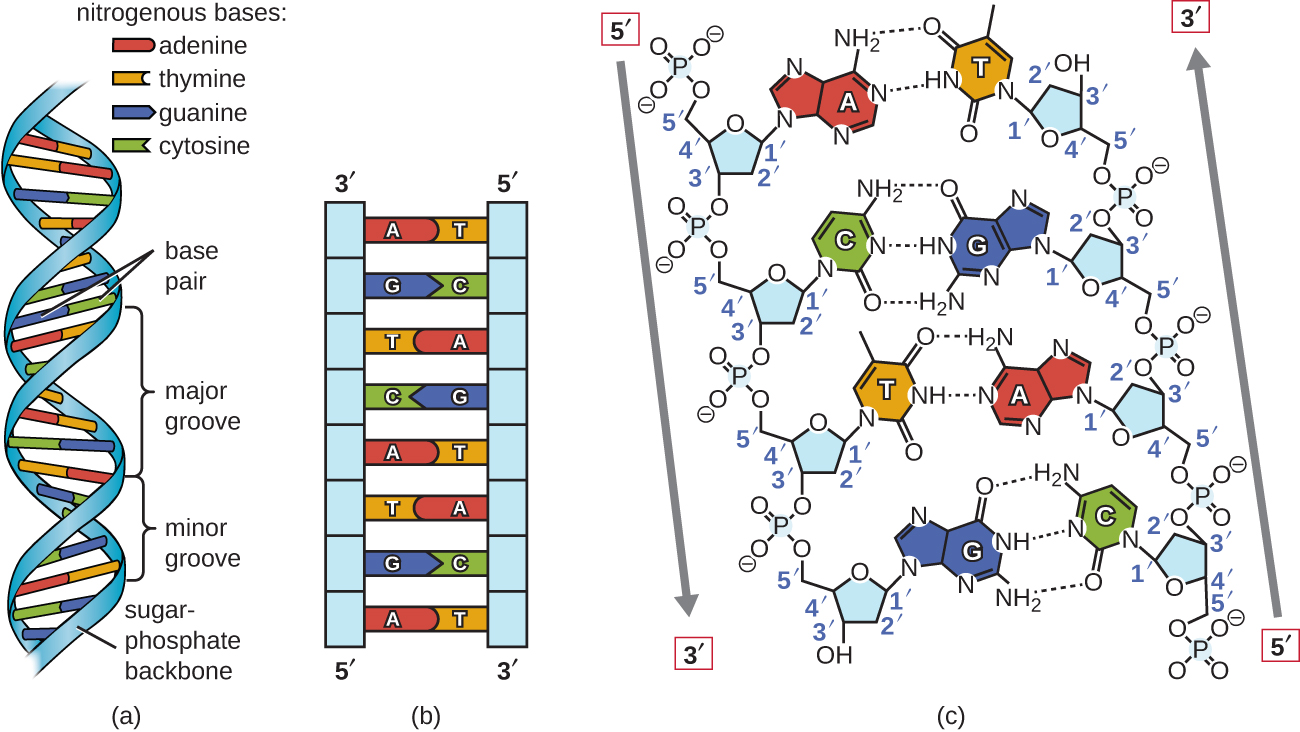
Draw and label a segment of dna showing its helix and complementary base pairing. Complementary Base Pairing | Rule & Examples - Study.com A segment of DNA has been unzipped to allow for complementary strands to be built. When cells enter into the cell division cycle, the DNA must be replicated prior to the division of the... Draw and label a segment of dna showing its helix and ... Jan 10, 2018 · The first image is a diagram that illustrates the base paring of DNA. First, there is the ribose-phosphate backbone that keeps the DNA together. Then the bases thymine and adenine are joined together by two hydrogen bonds. On the other hand, the bases guanine and cytosine are joined together by three hydrogen bonds. Base pairing - Structure of DNA - Higher Biology Revision - BBC The two strands of DNA are antiparallel which means that one strand runs in a 5' to 3' direction and the other runs in a 3' to 5' direction. This creates the twisting double helix structure of... DNA function & structure (with diagram) (article) | Khan Academy This selective binding is called complementary base pairing, and creates consistency in the nucleotide sequences of the two DNA polymers that join together to make a chromosome. This was first observed by Erwin Chargaff, who developed methods for counting nucleotides in DNA samples, and found that the percent of A nucleotides always equaled the percent of T nucleotides, and the percent of G nucleotides always equaled the percent of C nucleotides (within a margin of error).
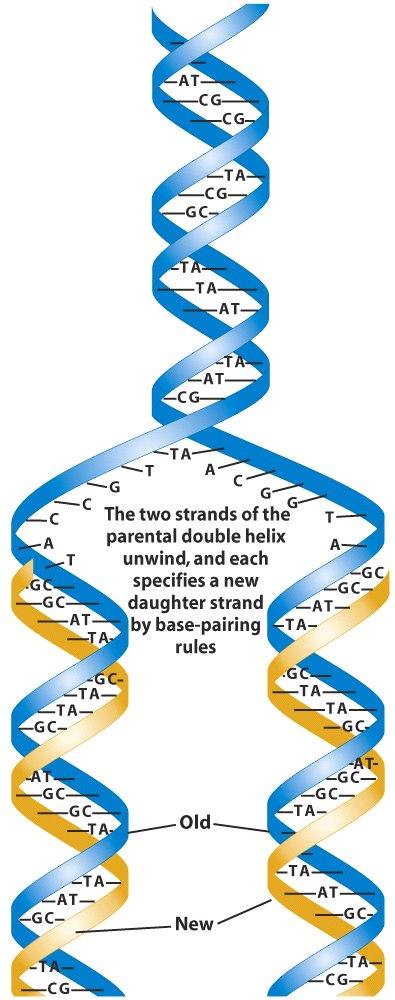
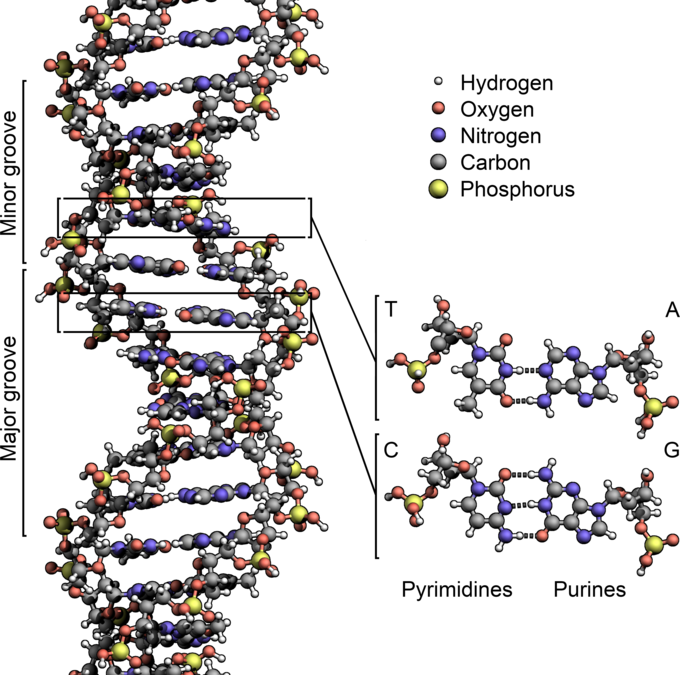
Base Pairing 2 - Department of Chemistry The most common pairing is with A, and this is what is found in the process of transcription, but G often forms base pairs with U in RNA molecules (See the DNA 2 module for descriptions of RNA and transcription). Remember, the one-ring bases are too small to form base pairs with each other. Please make your selection from the boxes at left above. DNA Replication Mechanisms - Molecular Biology of the Cell - NCBI Bookshelf Base-Pairing Underlies DNA Replication and DNA Repair. As discussed briefly in Chapter 1, DNA templating is the process in which the nucleotide sequence of a DNA strand (or selected portions of a DNA strand) is copied by complementary base-pairing (A with T, and G with C) into a complementary DNA sequence ().This process entails the recognition of each nucleotide in the DNA template strand by ... 2.5: B-Form, A-Form, and Z-Form of DNA - Biology LibreTexts Figure 2.5. 2: Antiparallel (a), plectonemically coiled (b, c, d) DNA strands. The arrows in a are pointed 3' to 5', but they illustrate the antiparallel nature of the duplex. The two strands of the duplex are antiparallel and plectonemically coiled. The nucleotides arrayed in a 5' to 3' orientation on one strand align with complementary ... Solved Question 3: Draw a picture, label, and describe the - Chegg Transcribed image text: Name: Assignment week 7 Question 3 Draw a picture, label, and describe the DNA double helix. Use the terms base. pairing, H-bonding, size-matching, pi-stacking, antiparallel, major groove, minor groove. You must include information on how the A:T and GC pairing is relevant to replication.
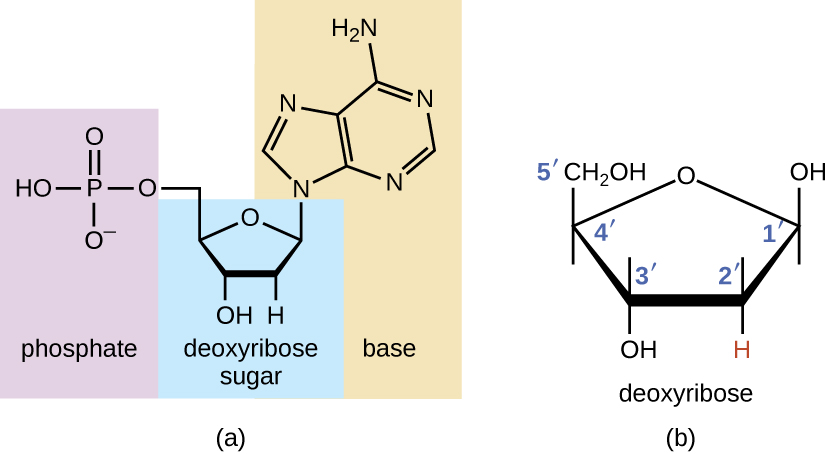
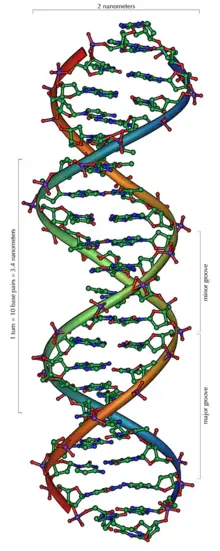
DNA structure and replication review (article) | Khan Academy DNA is only synthesized in the 5' to 3' direction. You can determine the sequence of a complementary strand if you are given the sequence of the template strand. For instance, if you know that the sequence of one strand is 5’-AATTGGCC-3’, the complementary strand must have the sequence 3’-TTAACCGG-5’. Base Pair - Genome.gov Jan 26, 2023 · A base pair consists of two complementary DNA nucleotide bases that pair together to form a “rung of the DNA ladder.” DNA is made of two linked strands that wind around each other to resemble a twisted ladder — a shape known as a double helix. Each strand has a backbone made of alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate groups. 9.1 The Structure of DNA - Concepts of Biology - 1st Canadian Edition The DNA molecule is a polymer of nucleotides. Each nucleotide is composed of a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar (deoxyribose), and a phosphate group. There are four nitrogenous bases in DNA, two purines (adenine and guanine) and two pyrimidines (cytosine and thymine). A DNA molecule is composed of two strands. DNA Replication (With Diagram) | Molecular Biology Basic Features of DNA Replication: All genetically relevant information of any DNA molecule is present in its sequence of bases on two strands. Therefore the main role of replication is to duplicate the base sequence of parent DNA molecule. The two strands have complementary base pairing. Adenine of one strand pairs with thymine of the opposite ...
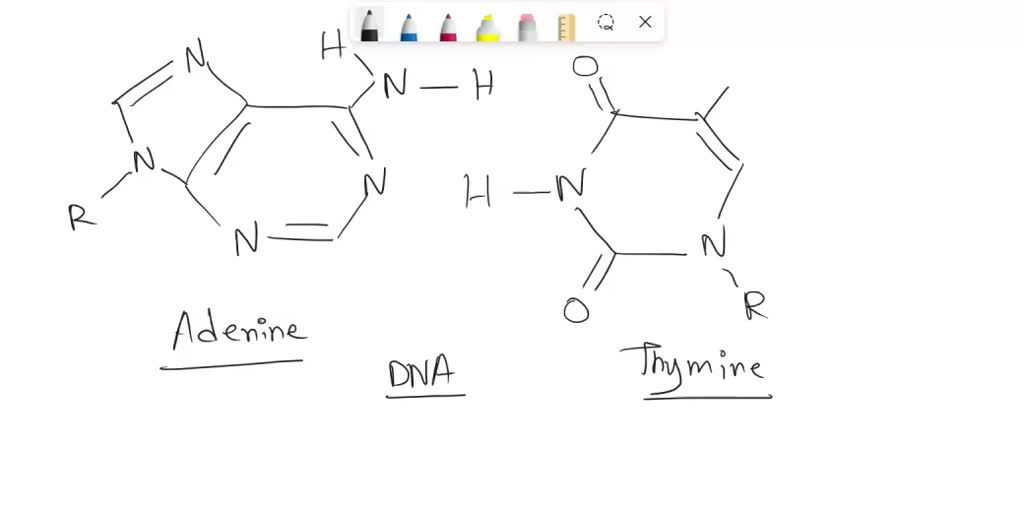
5.4: Base Pairing in DNA and RNA - Biology LibreTexts The answer: only with A & T and with C & G are there opportunities to establish hydrogen bonds (shown here as dotted lines) between them (two between A & T; three between C & G). These relationships are often called the rules of Watson-Crick base pairing, named after the two scientists who discovered their structural basis.
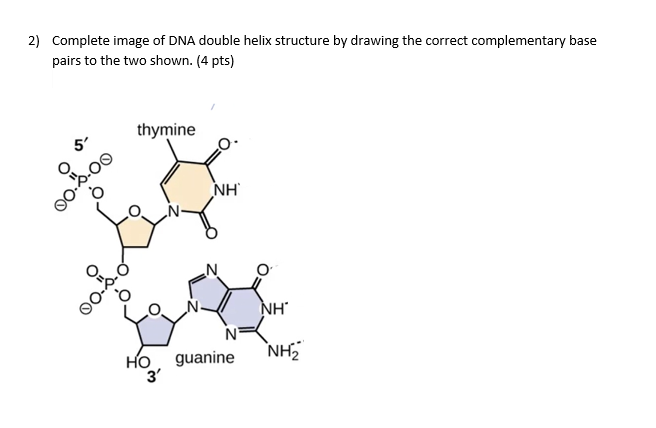
28.2: Base Pairing in DNA - The Watson-Crick Model Transcription, in which a segment of DNA is used to produce RNA. Translation, in which the information in RNA is translated into a protein sequence. Exercise 28.2. 1. For this short DNA segment, Identify the 5′ end and the 3′ end of the molecule. Circle the atoms that comprise the backbone of the nucleic acid chain.
What Is the Complementary Base Pairing Rule? | Sciencing This is called the complementary base pairing rule or Chargaff's rule. The Four Nitrogenous Bases In DNA nucleotide subunits, there are four nitrogenous bases: Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Cytosine (C) Guanine (G) Each of these bases can be divided into two categories: purine bases and pyrimidine bases. Adenine and guanine are examples of purine bases.
The Structure and Function of DNA - Molecular Biology of the Cell ... Each molecule of DNA is a double helix formed from two complementary strands of nucleotides held together by hydrogen bonds between G -C and A-T base pairs. Duplication of the genetic information occurs by the use of one DNA strand as a template for formation of a complementary strand.
DOC Chapter 12: RNA, DNA, and Protein Synthesis - COACH ANDERSON'S BLOG 1. Draw and label a segment of DNA showing its helix and complementary base pairing. 2. Indicate the sequence of the template strand of DNA if the non-template strand has the sequence: ATGGGGCGC 3. Describe the role of DNA helicase and DNA polymerase. 4. Summarize the process by which the DNA code is made into a protein. 5.
DNA Base Pair Types & Examples | What is a Base Pair? - Study.com DNA is the genetic material of the cell and contains all the information needed for cell structure and function. DNA is shaped like a double helix. It is made of two strands of nucleotides...
The Structure of DNA - University of Arizona Knowing the base pairing convention of A always pairing with T and G always pairing with C makes the complementary strand of the molecule understood. It is this feature of complementary base pairing that insures an exact duplicate of each DNA molecule will be passed to its daughter cells when a cell divides.
Nucleotide Structure: DNA Diagram - Science Trends The structure of DNA and RNA is also different. DNA is known for its double helix structure. The double helix is two strands that are intertwined with one another thanks to the complementary bases. RNA is a single-stranded molecule by contrast. The double helix form of DNA helps keep the genetic code intact.
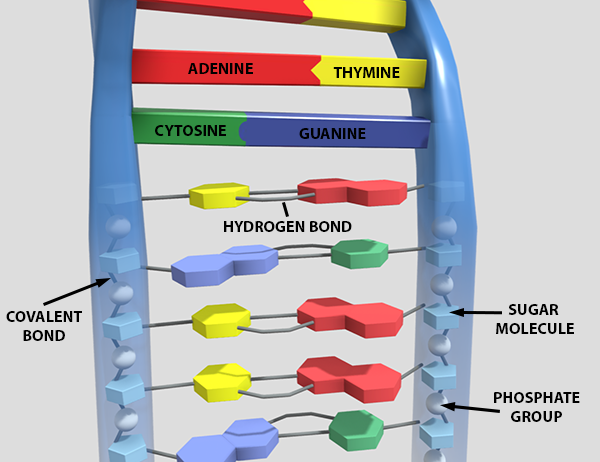
There Are 3 Types Of Bonds In DNA Double Helix Structure - ONLY ZOOLOGY TABLE OF CONTENTS↓↓↓↓↓↓. There Are 3 Types Of Bonds In DNA Double Helix Structure. 1. Glycosidic Bond: A Covalent Bond Between a Nitrogenous Base and Deoxyribose Pentose Sugar. 2. Phospho-diester Bond: A Covalent Bond Between two Deoxyribose Pentose Sugar. 3.
Draw and label a segment of DNA showing its helix and complementary ... One side is complementary, or completing the other side by fitting in the opposite nitrogen bases.The two strands of a double helix are described as complementary because the bases are in...
Double Helix - Genome.gov Jan 26, 2023 · A DNA molecule is made up of two linked strands that wind around each other to resemble a twisted ladder in a helix-like shape. Each strand has a backbone made of alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate groups. Attached to each sugar is one of four bases: adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) or thymine (T).
chapter 12 section 1 - Assessment Page 332 Mylena Riera... a. It needs to replicate itself. Thus it's a double strand, and the "new" strands form on each of the old strands to form a new double helix. The base pairingsensures that the new strand will be the exact counterpart to the old strand. b. It needs to be able to store a lot of information it its molecule. It does this with only 4 bases.
Draw and label a segment of DNA showing its helix and ... Draw and label a segment of DNA showing its helix and complementary base pairing. Solution Verified Create an account to view solutions By signing up, you accept Quizlet's Terms of Service and Privacy Policy Continue with Google Continue with Facebook Sign up with email Recommended textbook solutions Biology
bio pt 5 Flashcards | Quizlet radioactive labeling of bacteriophages - labeled proteins w/ radioactive phosphorus - labeled DNA w/ radioactive sulfer let the radioactive bacteriophages attack bacteria - only found traces of radioactive sulfur inside infected bacteria cells + Bacteriophage: virus that attacks bacteria RESULT: definitive evidence that DNA is genetic material






















Post a Comment for "40 draw and label a segment of dna showing its helix and complementary base pairing"